You’ve probably heard of Geofencing a location-based technology, but do you truly grasp the power it holds? It enables the creation of virtual perimeters around a geographic location using GPS or RFID technology. When someone crosses into or out of this virtual zone, you receive an alert. This opens a realm of possibilities for businesses and marketers.
Imagine triggering an action when a customer enters your store. You could send a welcome message, a coupon, or alert your sales staff. Upon their departure, a thank you message or survey could be sent. The possibilities are nearly endless.
The strength of this technology lies in its ability to connect the digital and physical realms. It adds context to location data, turning it into actionable insights. If you haven’t started utilizing this approach, you’re missing out on a transformative tool for your business. Why wait? Now is the time to harness this strategy for CDN!
What is Geofencing?
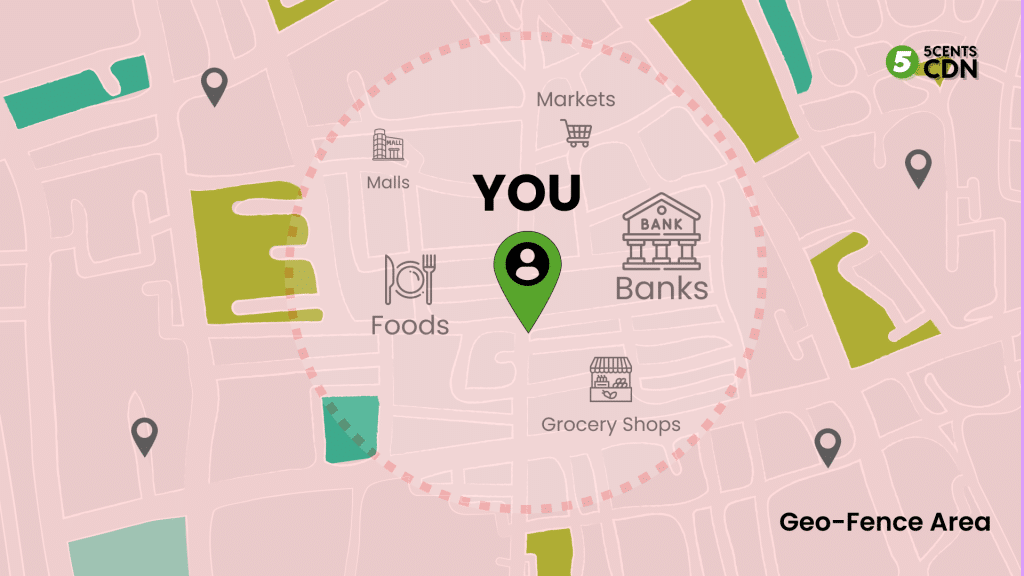
This approach leverages your location to create invisible perimeters around real-world sites. It uses your device’s GPS, Wi-Fi, or cellular data to detect when you cross these digital boundaries.
Entering or leaving a designated area triggers actions such as message or coupon delivery. For instance, many stores send deals when you’re nearby, enhancing customer engagement.
The applications are boundless, from tracking vehicles and equipment to managing events, complying with laws, optimizing advertising, and improving insights and sales.
How GeoFencing Works?
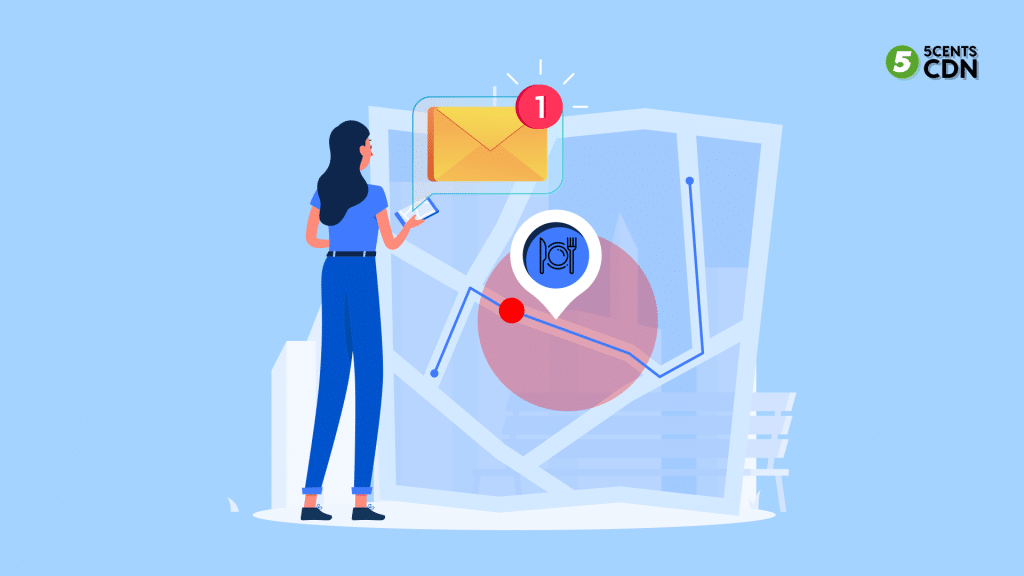
Setting this up involves defining the perimeter’s location and size on a map, then deciding the actions to occur when someone crosses the boundary. This could range from sending welcome messages to altering website content or prompting staff assistance.
Here’s a breakdown:
Defining the Boundary:
The user or administrator sets up a virtual boundary on a map, specifying the geographic area they want to cover. This could be done using GPS coordinates, Wi-Fi signals, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), or cellular data.
Location Tracking:
Devices within the geofenced area, such as smartphones or IoT (Internet of Things) devices, continuously transmit their location data.
Geofencing System:
It is a system or software monitors the location data and checks whether devices are inside or outside the predefined virtual boundary.
Triggered Actions:
When a device enters or exits the geofenced area, the system triggers predefined actions. These actions can include sending notifications, changing app behavior, or initiating specific processes.
Notification Delivery:
If a device enters the geofenced area, the system can send notifications or alerts to the user’s device. Conversely, when a device exits the area, it can trigger different actions or notifications.
Technological Components:
Geofencing utilize various technologies depending on the context. GPS is common for larger outdoor areas, while Wi-Fi or RFID might be used for more precise indoor geofencing.
Different Types:
There are various types of geofencing available, each suited to specific use cases. Here, are some different geofencing types for your consideration:
1. Circular:
This is the most common type, where the virtual boundary is defined in the shape of a circle. The center of the circle is marked by specific GPS coordinates, and the boundary extends outward in all directions.
Use Case: Circular geofencing is effective for scenarios where a simple, symmetrical boundary is sufficient, such as defining an area around a store or an event venue.
2. Polygonal:
In this type, the virtual boundary is created with multiple interconnected points, forming a polygon. This allows for more complex and irregular shapes compared to circular geofencing.
Use Case: Polygonal geofencing is suitable when the area to be covered has specific contours, like the boundaries of a park or a property with irregular edges.
3. Proximity:
Proximity geofencing focuses on the distance from a particular location, triggering actions when a device comes within a specified range. It doesn’t define a fixed boundary but rather considers the proximity to a central point.
Use Case: Proximity geofencing is useful for scenarios where the exact boundaries may not be critical, and actions are based on how close a device is to a central point, like sending notifications when a user is near a specific point of interest.
4. Dynamic:
Dynamic geofencing allows for real-time adjustments to the virtual boundary based on changing conditions. It adapts the geofence shape, size, or location dynamically to accommodate evolving circumstances.
Use Case: Dynamic geofencing is valuable in situations where the geofenced area needs to be flexible, such as during events where crowd sizes vary.
5. Time-Based:
Time-based geofencing involves setting up virtual boundaries that are active only during specific time intervals. Actions are triggered when a device enters or exits the geofenced area within the defined time frame.
Use Case: This type is beneficial for scenarios where geofencing actions need to be time-sensitive, like sending promotions only during business hours.
6. Wi-Fi:
Wi-Fi geofencing relies on Wi-Fi signals to determine a device’s location. It uses the availability and strength of Wi-Fi signals in an area to create virtual boundaries.
Use Case: Wi-Fi geofencing is useful indoors or in urban environments where GPS signals may be less reliable, such as shopping malls or airports.
By understanding these types of geofencing, businesses and applications can choose the most suitable approach based on their specific needs and use cases.
12 Benefits of GeoFencing
1) Targeted Marketing:
Geofencing enables businesses to send targeted and personalized messages or promotions to users when they enter a specific geographic area, improving the relevance of marketing efforts.
2) Increased Engagement:
By delivering timely and location-specific notifications, geofencing enhances user engagement with mobile apps, leading to increased interaction and brand awareness.
3) Improved Customer Experience:
Location-based alerts and services, such as personalized recommendations or special offers when customers are near a store, contribute to an enhanced and tailored customer experience.
4) Enhanced Security:
Geofencing can be used for security purposes, triggering alerts or actions when a device enters or exits a predefined area. This is valuable for monitoring assets, tracking vehicles, or ensuring the safety of individuals.
5) Efficient Resource Management:
Businesses can optimize resource allocation and operational efficiency by using geofencing to track and manage the movement of vehicles, equipment, or personnel in real-time.
6) Increased Sales Opportunities:
By sending targeted promotions or discounts to users when they are in proximity to a store or point of sale, geofencing creates opportunities to boost sales and conversions.
7) Enhanced Data Collection:
Geofencing generates valuable location-based data, providing businesses with insights into customer behavior, preferences, and movement patterns, which can inform strategic decision-making.
8) Event Management:
Geofencing is beneficial for managing events by delivering real-time information, updates, and promotions to attendees based on their location within the event venue.
9) Geographically-Tailored Content Delivery:
Content delivery networks (CDNs) use geofencing to optimize the delivery of digital content, ensuring faster load times and a seamless experience for users in specific geographic regions.
10) Cost-Effective Advertising:
Businesses can optimize advertising budgets by targeting specific geographic areas with relevant promotions, reducing the cost per impression and increasing the effectiveness of campaigns.
11) Real-Time Analytics:
Geofencing provides businesses with real-time analytics, allowing them to track and analyze user interactions, foot traffic, and the effectiveness of location-based campaigns.
12) Compliance with Regulations:
Geofencing can help businesses comply with location-specific regulations, such as adhering to privacy laws or ensuring that certain content is accessible only in approved regions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this technology is more than just a tool; it’s a game-changer in how digital interactions are integrated with physical movements. It not only enhances user experiences but also opens new avenues for business innovation and efficiency. Try using this features with 5centsCDN now!