Geo Proximity rules allow system administrators to specify the location or the longitude & latitude of their hosted servers (data center locations). Once configured, the traffic director will automatically calculate which server is closest to the end-querying client in real-time. Geo Proximity can also be used with Failover and is highly customizable and scalable.
Geo Proximity rules are most commonly used for optimizing resolution accuracy and speeds. With the ability to configure rules based on precise geographic-specific information, end users will have the fastest possible connection and an enhanced overall experience when interacting with your domain.
-> How to Configure Geo Proximity Rules in Traffic Director?
- Login to 5centsCDN control panel.
- Go to Traffic Director.
- Click the Manage button of your domain.
- On the redirected page, you can see all the records. Click the green plus button to create a new record.
- We can enable Geo Proximity for A, AAAA, CNAME, and ANAME records. So select any one of these from the list.
- Provide the following details in the redirected window.
- Name: Provide the hostname(For example www).
- TTL: Specify the corresponding TTL value. Time to live (TTL) dictates how long your records stay cached. For example, for how long will your A record is cached before retrieving a new copy of the record from DNS servers
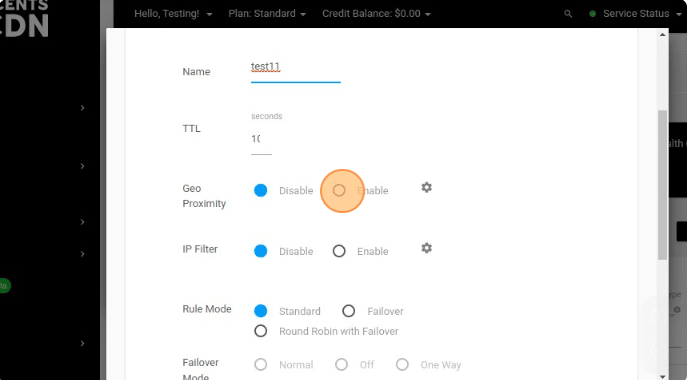
- Geo Proximity: We can configure the Geo location here. configure the following settings
- Click the Enable button.
-
-
- Click the Settings Icon.
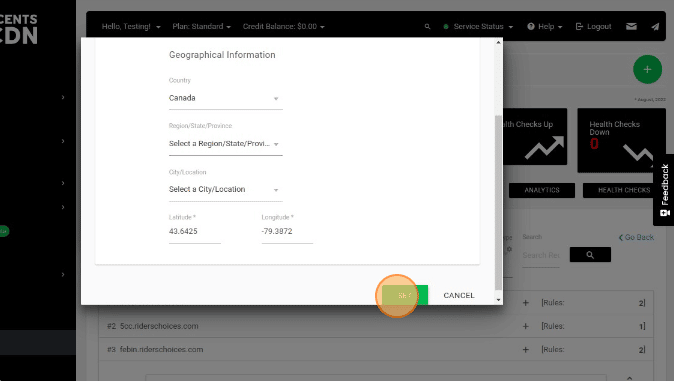
- Name – Provide a name for the location.
- Geographical Information – You can select the geographic details such as country, region, state, province, and city.
- The Latitude and Longitude will be calculated based on your location selection.
- Click the SET button.
- Click the Settings Icon.
-
-
- IP Filter: We cannot enable IP Filter if the Geo Proximity is enabled. So it will be disabled automatically.
- Rule Mode: choose the appropriate rule mode.
- Standard – In standard rule mode, you can point your domain to an IP/Hostname. This method does not allow failure switching between servers. Specify all the IP/Hostname in the field and you can enable or disable them manually.
- Failover– This rule method allows you to add multiple servers’ IP addresses or hostnames. The traffic director will check the status of your server periodically using Health Check and switch to another server if the primary goes offline based on the failover mode. The failover modes are explained below.
- Normal – Failover will attempt to use the lowest IP address/Hostname in the queue. This means if the lowest IP/Hostname becomes available again then it will switch to the lowest IP/hostname address.
- Off- Failover will turn off after the first and only event has occurred. If the primary IP/hostname becomes available again, it won’t switch back. You have to resave the settings again to use the primary IP/Host.
- One Way- Failover will only move further down the queue to the higher IP/Hostname. If the lower one becomes available. It won’t use it. You have to resave the settings again to use the primary IP/Hostname.
- Round Robin with Failover- When using the Standard and Failover methods, the response will be received by a specific IP address or Hostname at a time. Round Robin with failover mode acts as a load balancer and provides random responses from active IP addresses or Hostname. Ensure you have enabled Health Check for the IP/Hostname.
- Click the CREATE button.
The DNS record is created successfully. Now you can create multiple rules to same the records to direct traffic in different locations. Suppose, If you have configured the CANADA region in the above configuration. Then the traffic from worldwide will direct to the specified IP address or Hostname in the above settings.
If you want to redirect traffic from INDIA to a different IP or Hostname, then you have to create another rule under the same record using Geo Proximity. The other locations will be direct to the geographically nearest server, which means if a user requests from SINGAPORE will be direct to the server configured for INDIA.
